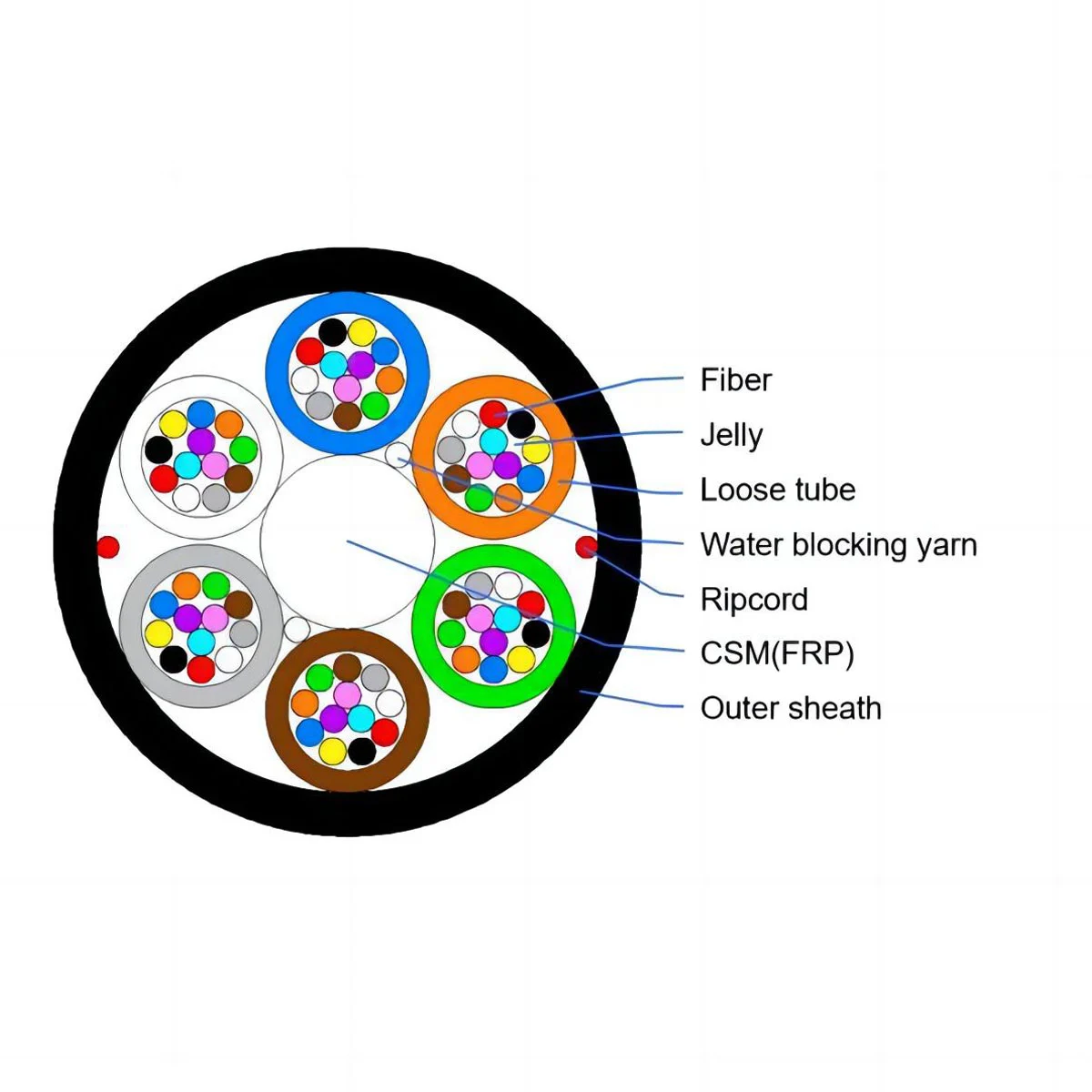
Classification of Optical Jumper Cords
Optical jumper cords are mainly classified into three types based on the termination type: ST-ST, SC-SC, ST-SC.
According to the type of fiber, they are classified into two main types: single-mode fiber and multi-mode fiber. The patch cord specifications include 0.5m, 1m, 2m, 3m, 5m, and 10m.
Based on the material of the cable outer sheath, they can be classified into ordinary type, ordinary flame-retardant type, low smoke zero halogen type (LZSH), and low smoke zero halogen flame-retardant type, etc.
In accordance with the fire protection level of buildings and the fire resistance requirements of materials, appropriate measures should be taken in the structured cabling system.
In flammable areas and building risers where cables or optical fibers are deployed, flame-retardant cables and optical fibers should be used;
In large public places, it is advisable to use flame-retardant, low smoke, low toxicity cables or optical fibers;
Flame-retardant distribution equipment should be used between adjacent equipment rooms or junction rooms.
The receiving and transmitting wavelengths of the optical modules at both ends of the optical jumper cord must be consistent, which means that the optical modules at both ends of the optical fiber must have the same wavelength. A simple way to distinguish this is that the colors of the optical modules should be the same.
Do not bend or loop the optical fiber excessively during use, as this will increase attenuation during transmission.
After using the optical jumper cord, be sure to protect the optical fiber connector with a protective sleeve. Dust and oil contamination can degrade the optical fiber's coupling performance. If the optical fiber connector becomes dirty, it can be cleaned with a cotton swab dipped in alcohol, otherwise, it will affect communication quality.
Before use, the ceramic ferrule and the end face of the ferrule of the optical jumper cord must be wiped clean with alcohol and degreased cotton.
During use, the minimum bending radius of the optical fiber should be less than 30mm.
Protect the ferrule and the end face of the ferrule to prevent scratches and contamination. Attach a dust cap immediately after disassembling.
Do not directly view the fiber end face when the laser signal is being transmitted.
If damage due to human or other uncontrollable factors occurs, the damaged optical jumper cord should be replaced promptly.
If there is an abnormal situation in the optical fiber network or system, the fault can be troubleshooted by testing each component one by one. When testing or troubleshooting patch cord faults, continuity tests can be performed first. Usually, a visible laser pen can be used to determine the entire optical fiber link. Alternatively, a precise optical fiber insertion loss and return loss meter can be used to test various indicators. If the indicators are within the acceptable range, the patch cord is normal; otherwise, it is not.